ANN with Keras
import numpy as np
from random import randint
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
train_labels = []
train_samples = []
Example data:
- An experimental drug was tested on indivisuals from ages 13 to 100 in a clinical trial.
- The trial had 2100 participants. Half were under 65 years old, haf were 65 years or older.
- Around 95% of patients 65 or older experienced side effects.
- Around 95% of patients under 65 experienced no side effects.
for i in range(50):
# The ~5% of younger indivisuals who did experience side effects
random_younger = randint(13, 64)
train_samples.append(random_younger)
train_labels.append(1) # 부작용 라벨 1
# The ~5% of older indivisuals who did not experience side effects
random_older = randint(65, 100)
train_samples.append(random_older)
train_labels.append(0) # 안부작용 라벨 0
for i in range(1000):
# The ~95% of younger indivisuals who did not experience side effects
random_younger = randint(13,64)
train_samples.append(random_younger)
train_labels.append(0)
# The ~95% of older indivisuals who did experience side effects
random_older = randint(65, 100)
train_samples.append(random_older)
train_labels.append(1)
for i in train_samples:
print(i)
13
92
31
90
…
…
…
43
65
54
99
for i in train_labels:
print(i)
1
0
1
0
…
…
…
0
1
0
1
텐서플로우 문서-tf.keras에 들어가면 지원하는 데이터 타입을 확인할 수 있다.
train_labels = np.array(train_labels)
train_samples = np.array(train_samples)
train_labels, train_samples = shuffle(train_labels, train_samples)
# rescale 13 to 100 -> 0 to 1
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1))
scaled_train_samples = scaler.fit_transform(train_samples.reshape(-1,1))
for i in scaled_train_samples:
print(i)
[0.28735632]
[0.68965517]
[0.20689655]
[0.2183908]
…
[0.2183908]
[0.91954023]
[0.32183908]
[0.02298851]
# Create an ANN with Keras API
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Activation, Dense
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.metrics import categorical_crossentropy
# identifying your GPU
physical_devices = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices('GPU')
print("Num GPUs Available: ", len(physical_devices))
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_devices[0], True)
Num GPUs Available: 0
# Create Sequential Model's architecture
model = Sequential([
Dense(units=16, input_shape=(1,), activation='relu'),
Dense(units=32, activation='relu'),
Dense(units=2, activation='softmax') # final output(2 class)
])
model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 16) 32
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 32) 544
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 2) 66
=================================================================
Total params: 642
Trainable params: 642
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
# ready for training
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.0001), loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x=scaled_train_samples, y=train_labels, batch_size=10, epochs=30, shuffle=True, verbose=2)
# verbose : adjust the level of showing train process
Epoch 1/30
210/210 - 0s - loss: 0.6635 - accuracy: 0.5290
Epoch 2/30
210/210 - 0s - loss: 0.6321 - accuracy: 0.6233
Epoch 3/30
210/210 - 0s - loss: 0.5980 - accuracy: 0.6905
…
…
…
Epoch 28/30
210/210 - 0s - loss: 0.2739 - accuracy: 0.9333
Epoch 29/30
210/210 - 0s - loss: 0.2724 - accuracy: 0.9371
Epoch 30/30
210/210 - 0s - loss: 0.2713 - accuracy: 0.9362
“<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fe495a43a00>”
# what if we add the validation option
model.fit(x=scaled_train_samples, y=train_labels, validation_split=0.1, batch_size=10, epochs=30, shuffle=True, verbose=2)
# 검증 데이터는 셔플되지 않음
# val set과 train set의 metrics가 비슷하다면 generalization 잘 된 것임
Epoch 1/30
189/189 - 0s - loss: 0.2759 - accuracy: 0.9360 - val_loss: 0.2220 - val_accuracy: 0.9524
Epoch 2/30
189/189 - 0s - loss: 0.2749 - accuracy: 0.9360 - val_loss: 0.2204 - val_accuracy: 0.9524
Epoch 3/30
189/189 - 0s - loss: 0.2741 - accuracy: 0.9360 - val_loss: 0.2213 - val_accuracy: 0.9524
…
…
…
Epoch 28/30
189/189 - 0s - loss: 0.2646 - accuracy: 0.9487 - val_loss: 0.2068 - val_accuracy: 0.9524
Epoch 29/30
189/189 - 0s - loss: 0.2645 - accuracy: 0.9381 - val_loss: 0.2081 - val_accuracy: 0.9667
Epoch 30/30
189/189 - 0s - loss: 0.2644 - accuracy: 0.9460 - val_loss: 0.2071 - val_accuracy: 0.9667
“<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fe495df9970>”
Test Set 만들기
# create the test set
test_labels = []
test_samples = []
for i in range(10):
# The ~5% of younger indivisuals who did experience side effects
random_younger = randint(13, 64)
test_samples.append(random_younger)
test_labels.append(1) # 부작용 라벨 1
# The ~5% of older indivisuals who did not experience side effects
random_older = randint(65, 100)
test_samples.append(random_older)
test_labels.append(0) # 안부작용 라벨 0
for i in range(200):
# The ~95% of younger indivisuals who did not experience side effects
random_younger = randint(13,64)
test_samples.append(random_younger)
test_labels.append(0)
# The ~95% of older indivisuals who did experience side effects
random_older = randint(65, 100)
test_samples.append(random_older)
test_labels.append(1)
test_labels = np.array(test_labels)
test_samples = np.array(test_samples)
test_labels, test_samples = shuffle(test_labels, test_samples)
scaled_test_samples = scaler.fit_transform(test_samples.reshape(-1,1))
Predict
predictions = model.predict(x=scaled_test_samples, batch_size=10, verbose=0)
for i in predictions:
print(i)
# 1. not experiencing a side effect 2. experiencing a side effect
[0.23556748 0.7644325 ]
[0.96136826 0.03863173]
[0.10682783 0.8931722 ]
[0.96758014 0.03241989]
…
…
…
[0.06094055 0.9390595 ]
[0.01254966 0.98745036]
[0.01254966 0.98745036]
[0.01874658 0.98125345]
rounded_predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=-1)
for i in rounded_predictions:
print(i)
1
0
1
0
…
…
…
0
1
0
1
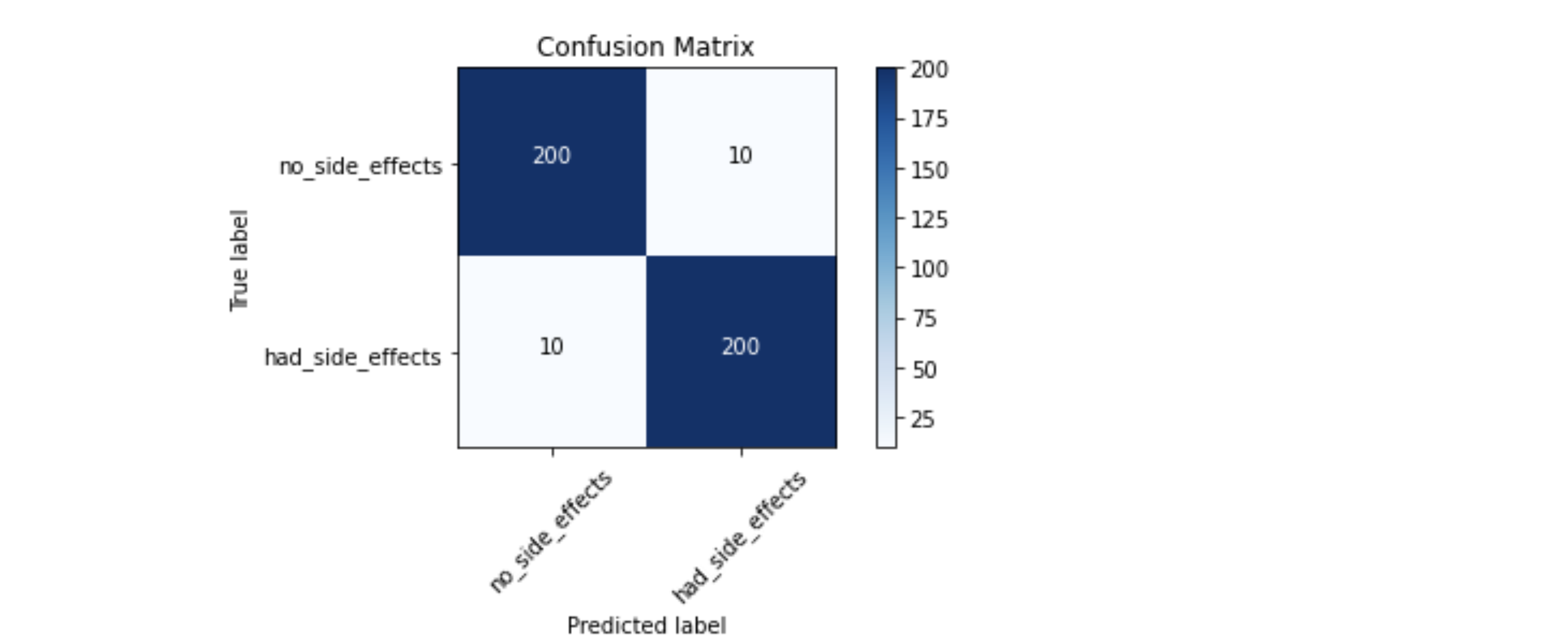
Create the Confusion Matrix to see how the model well predicted the test data
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import itertools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true=test_labels, y_pred=rounded_predictions)
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float')/cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
print("Normalized confusion matrix")
else:
print("Confusion matrix, without normalization")
print(cm)
thresh = cm.max()/2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j,i,cm[i,j],
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i,j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
cm_plot_labels = ['no_side_effects', 'had_side_effects']
plot_confusion_matrix(cm=cm, classes=cm_plot_labels, title='Confusion Matrix')
Confusion matrix, without normalization
[[200 10]
[ 10 200]]
Save and Load a Model
model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 16) 32
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 32) 544
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 2) 66
=================================================================
Total params: 642
Trainable params: 642
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
# model.save()
# Checks first to see if file exists already
import os.path
if os.path.isfile('models/medical_trial_model.h5') is False:
model.save('models/medical_trial_model.h5')
This save functions saves:
- The architecture of the model, allowing to re-create the model.
- The weights of the model.
- The training configuration(loss, optimizer).
- The state of the optimizer, allowing to resume training exactly where you left off.
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
new_model = load_model('models/medical_trial_model.h5')
new_model.summary()
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 16) 32
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 32) 544
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 2) 66
=================================================================
Total params: 642
Trainable params: 642
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
new_model.get_weights()
[array([[ 0.3521593 , 0.17914219, 0.64067507, -0.5047269 , -0.5019833 ,
-0.21913806, 0.02865078, 0.31927818, 0.6358836 , -0.16967988,
0.6617938 , -0.54656065, -0.25711647, -0.54121 , -0.28327456,
0.7206835 ]], dtype=float32),
array([-0.15370801, 0.06439009, -0.06952863, 0. , 0. ,
0. , 0.23023002, -0.14227156, -0.18356611, 0. ,
-0.17873147, 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,
-0.20324457], dtype=float32),
array([[-3.86920273e-01, 1.57447681e-01, 4.99442488e-01,
-4.90225740e-02, 4.44448441e-01, -5.92532218e-01,
3.07509452e-01, -2.27273762e-01, -4.06039655e-01,
…
…
…
[-0.5413718 , 0.3335405 ],
[ 0.7702613 , -0.5420549 ],
[-0.46344241, 0.07125077],
[-0.5357425 , 0.03514996]], dtype=float32),
array([ 0.14117242, -0.14117241], dtype=float32)]
new_model.optimizer
“<tensorflow.python.keras.optimizer_v2.adam.Adam at 0x7fe495d709a0>”
model.to_json()
If you only need to save the architecture of a model, and not it’s weights or it’s training configuration, you can use the following fuction to save the architecture only.
# save as json
json_string = model.to_json()
# save as yaml
# yaml_string = model.to_yaml()
json_string
’{“class_name”: “Sequential”, “config”: {“name”: “sequential”, “layers”: [{“class_name”: “InputLayer”, “config”: {“batch_input_shape”: [null, 1], “dtype”: “float32”, “sparse”: false, “ragged”: false, “name”: “dense_input”}}, {“class_name”: “Dense”, “config”: {“name”: “dense”, “trainable”: true, “batch_input_shape”: [null, 1], “dtype”: “float32”, “units”: 16, “activation”: “relu”, “use_bias”: true, “kernel_initializer”: {“class_name”: “GlorotUniform”, “config”: {“seed”: null}}, “bias_initializer”: {“class_name”: “Zeros”, “config”: {}}, “kernel_regularizer”: null, “bias_regularizer”: null, “activity_regularizer”: null, “kernel_constraint”: null, “bias_constraint”: null}}, {“class_name”: “Dense”, “config”: {“name”: “dense_1”, “trainable”: true, “dtype”: “float32”, “units”: 32, “activation”: “relu”, “use_bias”: true, “kernel_initializer”: {“class_name”: “GlorotUniform”, “config”: {“seed”: null}}, “bias_initializer”: {“class_name”: “Zeros”, “config”: {}}, “kernel_regularizer”: null, “bias_regularizer”: null, “activity_regularizer”: null, “kernel_constraint”: null, “bias_constraint”: null}}, {“class_name”: “Dense”, “config”: {“name”: “dense_2”, “trainable”: true, “dtype”: “float32”, “units”: 2, “activation”: “softmax”, “use_bias”: true, “kernel_initializer”: {“class_name”: “GlorotUniform”, “config”: {“seed”: null}}, “bias_initializer”: {“class_name”: “Zeros”, “config”: {}}, “kernel_regularizer”: null, “bias_regularizer”: null, “activity_regularizer”: null, “kernel_constraint”: null, “bias_constraint”: null}}]}, “keras_version”: “2.5.0”, “backend”: “tensorflow”}’
# model reconstruction from json:
from tensorflow.keras.models import model_from_json
model_architecture = model_from_json(json_string)
# model reconstruction from yaml
# from tensorflow.keras.models import model_from_yaml
# model = model_from_yaml(yaml_string)
model_architecture.summary()
# remember that this only loads the architecture.
# you need to adjust the weights, optimizer, loss...etc, from the scratch
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 16) 32
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 32) 544
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 2) 66
=================================================================
Total params: 642
Trainable params: 642
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
model.save_weights()
If you only need to save the weights of a model, you can use the following function save the weights only.
# Checks first to see if file exists already
import os.path
if os.path.isfile('models/my_model_weights.h5') is False:
model.save_weights('models/my_model_weights.h5')
model2 = Sequential([
Dense(units=16, input_shape=(1,), activation='relu'),
Dense(units=32, activation='relu'),
Dense(units=2, activation='softmax')
])
model2.load_weights('models/my_model_weights.h5')
model2.get_weights()
[array([[ 0.3521593 , 0.17914219, 0.64067507, -0.5047269 , -0.5019833 ,
-0.21913806, 0.02865078, 0.31927818, 0.6358836 , -0.16967988,
0.6617938 , -0.54656065, -0.25711647, -0.54121 , -0.28327456,
0.7206835 ]], dtype=float32),
array([-0.15370801, 0.06439009, -0.06952863, 0. , 0. ,
0. , 0.23023002, -0.14227156, -0.18356611, 0. ,
-0.17873147, 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,
-0.20324457], dtype=float32),
array([[-3.86920273e-01, 1.57447681e-01, 4.99442488e-01,
-4.90225740e-02, 4.44448441e-01, -5.92532218e-01,
3.07509452e-01, -2.27273762e-01, -4.06039655e-01,
…
…
…
[-0.5413718 , 0.3335405 ],
[ 0.7702613 , -0.5420549 ],
[-0.46344241, 0.07125077],
[-0.5357425 , 0.03514996]], dtype=float32),
array([ 0.14117242, -0.14117241], dtype=float32)]