Performance analysis in Python - 성능 분석
Choose the right data structure for the right situation.
Algorithm performance analysis : how to compare?
2 solutions:
- To evaluate the performance, you can manually evaluate the time performance of the operation. It’s not feasible in real life conditions. ❌
- Set a criterion and compare 2 functions relative to it: how many operations are done? With this measure, regardless of the environment, we can estimate the performance of an algorithm.
# Calculations Frequency
def func(arr,init):
n = len(arr) # 1 1
ret = init # 1 1
for i in range(n): # 1 n
ret += arr[i] # 1 n
return ret # 1 1
# 2n+3
arr = [1,2,3,4]
result = func(arr,10)
print(result)
Output = 25
-
Number of operations :
\[T(n) = 2n+3\] -
It is an over easy situation. Real life case isn’t that straightforward. + performance interpretation is ambiguous..
Compare performance with Big O
→ Determine according to how big is the work (size of data) how much time the code will take to fully execute
→ How code slows as data grows, regardless of hardware.
→ x data takes 1 hour t complete. 2x data ≠ 2 hours, depending of the code has to do.
→ Big O measures the worst case scenario, Big Omega Ω(n) the best case scenario.
→ Big Theta Θ(n) describes algorithms that met best and worst case sceniarios.
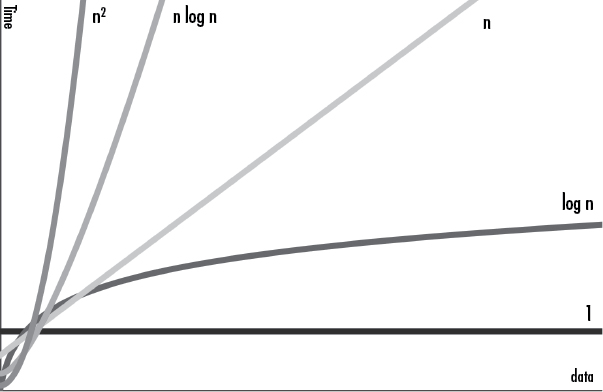
Big O orders - with bookshelf comparison
-
Constant time - lowest order - fast algorithm
\[O(1)\]Example: check if bookshelf is empty. If we see 1 book: the bookshelf is not empty and algorithms stops. Always same runtime.
-
Logarithmic time - fast algorithm
\[O(log\ n)\]Example: searching for 1 book in an alphabetically sorted bookshelf. Pick middle book: is th eone i want before or after that letter? This has reduced search range by half. Repeat until found. With this order, even if workload doubles, the runtime increases by one step (bc logarithmic search)
-
Linear time - average algorithm
\[O(n)\]Example: If you try to read all books on the bookshelf, it will take x time: Reading twice as many books whould take 2x.
-
N-log-N time - average algorithm
\[O(n \ log \ n)\]Example: Must sort books in alphabetical order. Sorting one book is a O(log n) operation, that has to be done as many times as there are books: O(log n) * O(n).
-
Polynomial time - slow algorithm
\[O(n^2)\]Example: Finding a duplicate book in unsorted bookshelf: take 1st book, compare it to all the others. Then repeat with 2nd book. It takes the squared number of books operations to finish the algorithm. If an O(n) or O(n log n) algorithm exists, it is a better solution.
-
Exponential time - slow algorithm
\[O(2^n)\]Example: take photos of every possible book combination (1 order) on the bookshelf:
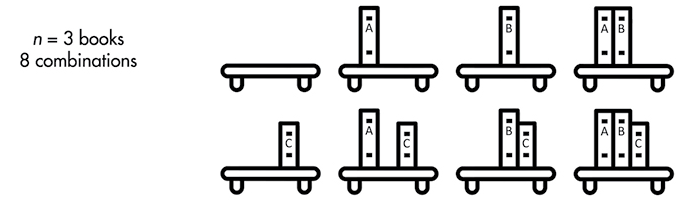
-
Factorial time - highest order - slow algorithm
\[O(n!)\]Example: take photos of every possible book order on the bookshelf:
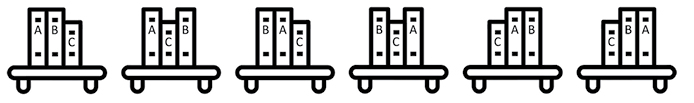
Representation of the computing time for all Big O orders
What is the Big O order of the code?
Looking at the previous code:
# Calculations Frequency
def func(arr,init):
n = len(arr) # 1 1
ret = init # 1 1
for i in range(n): # 1 n
ret += arr[i] # 1 n
return ret # 1 1
# 2n+3
arr = [1,2,3,4]
result = func(arr,10)
print(result)
The Big O order here is O(n), because: lower order terms and coefficients are dropped.
Why drop lower order terms?
As n grows, they become less significant.
Why drop coefficients?
As n grows, their impact on computation time becomes negligible.
⚠️ Big O only takes into account the number of operations in the code, withaout looking at other factors such as computer speed, data locations (RAM vs HDD)…
What is an Abstract Data Type (ADT)?
As opposed to a data structure, an ADT is a data type that will work independently of the implementation details (choice of programming language). The ADT is defined by what operations should be performed, not how they should be implemented.
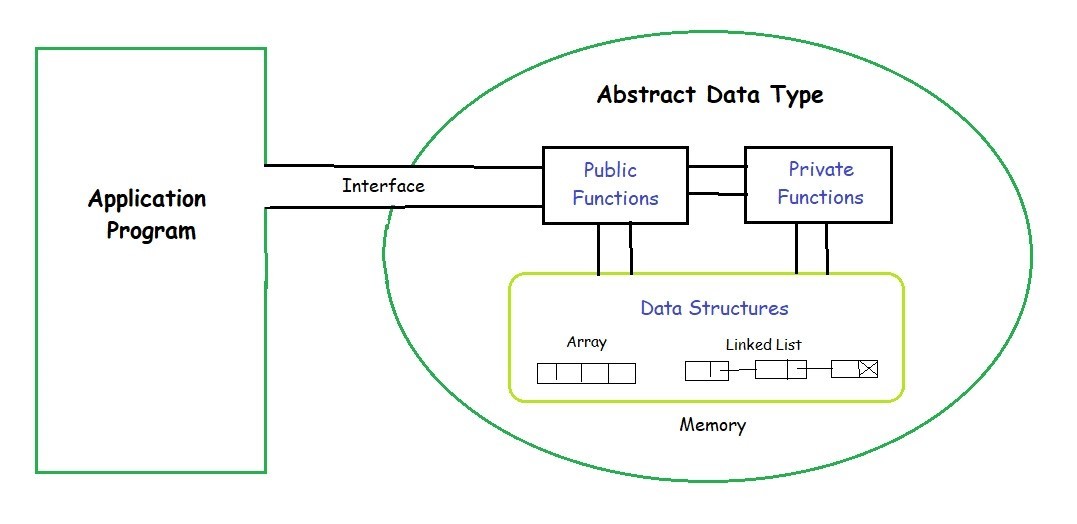
The user can make use of certain data types like Int, float, char. The user only needs to know he can use them, no need to know how at a deeper level.
Sources
https://inventwithpython.com/beyond/chapter13.html
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/abstract-data-types/
https://www.reddit.com/r/explainlikeimfive/comments/4iffoh/eli5_what_is_an_abstract_data_type_adt/